by
Michael Buehler, Thorsten Jelinek, Sergio Gusmao Suchodolski & Olivier M. Schwab*
What is the New Silk Road?
Today, China is breathing new life into the Silk Road with the goal of forging stronger relationships with its neighbours through the development and sharing of resources. President Xi Jinping, speaking at the World Economic Forum 2017 in Davos, referred to the ancient Silk Road, highlighting the fact that international trade is an inherent human activity that helped in the past to maintain peace and stability over long periods of time.
What is its potential?
Today, the New Silk Road, or what is known as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), has the potential to prompt a profound shift in the global order towards a new multilateralism. In a narrow sense, the BRI is primarily a strategic infrastructure initiative of historic proportions.
The planning and delivery of scalable infrastructure for power generation, transportation, water supply, and telecommunications will bring much-needed economic and societal connectivity to the 65 countries along this new network.
Through the BRI, China is proposing to share its immense financial and industrial resources and capabilities, as well as its experience of four decades of reform and opening-up, while securing its own long-term development.
The BRI has five major goals: policy coordination; facilities’ connectivity; unimpeded trade; financial integration; and people-to-people exchange. Beyond the initial commitment by the Chinese government of about $1 trillion in infrastructure development, which conservative estimates believe to be viable, the BRI will require roughly an aggregate of $6 trillion for the next 15 years to finance infrastructure projects fuelling the Belt and Road economies.
During that period, the Chinese plan to cumulatively invest $4 trillion in total – about 20 times the size of the post-Second World War Marshall Plan investment of $17 billion, which has a value of about $190 billion today. Several multilateral development banks have also committed to support the BRI to accomplish those ambitious goals and finance BRI-related projects.
What are the eight steps towards shared prosperity and a sustainable future?
To avoid being locked into unsustainable patterns of development, which has been the common pitfall of large-scale strategic infrastructure projects, we anticipate eight transformation factors that have the potential to provide high-level stewardship for the BRI and revive the spirit of shared prosperity. These insights are derived from several years of analysing the infrastructure industry and its development projects.
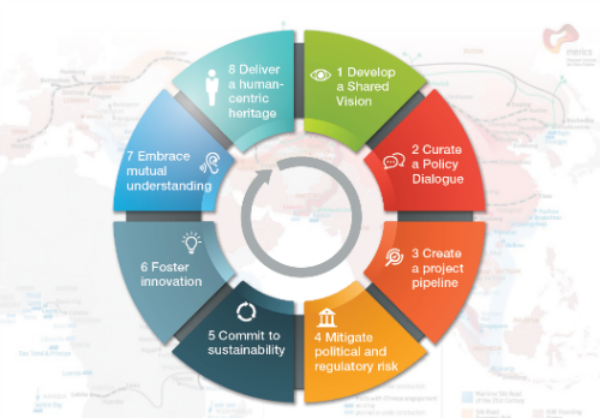
1. Shared vision: Achieving transnational and international support for a shared vision for strategic infrastructure development that promotes wellbeing and a national sense of purpose to the communities beyond national borders.
2. Multilateralism: Curating an open and multilateral policy dialogue that addresses public-private-civic cooperation, early-stage project financing, standardized procurement and transparency, to level the playing field and build trusted relationships.
3. Project-preparation facility: Creating an infrastructure project-preparation facility to ensure a pipeline of bankable projects and a transnational centre of excellence to deliver the largest portfolio of projects ever.
4. Risk mitigation: Proactively mitigating political and regulatory risk to boost stakeholder engagement and confidence in the plan by investors, off-takers and operators.
5. Sustainable development: Committing to sustainability, inclusion and affordability principles to generate value for future generations beyond Agenda 2030.
6. Innovation: Enhancing technological and business model innovation for sustained value creation, ensuring readiness for the future.
7. People-to-people exchange: Governing domestic and cross-border migration and promoting mutual learning and understanding, to enable and deepen people-to-people exchange and transnational cultural cooperation, ensuring transcendent growth and universal purpose.
8. Human-centric and future-ready: Delivering the new humane infrastructure heritage beyond the current infrastructure usage for the next millennium.
* Michael Buehler is Head of Infrastructure & Urban Development at World Economic Forum
Thorsten Jelinek is Director at Taihe Institute
Sergio Gusmao Suchodolski is Director General, Strategy and Partnerships at New Development Bank (NDB)
Pedro Rodrigues De Almeida is Member, B20 Task Force on Financing Growth & Infrastructure at B20 Germany
Olivier M. Schwab is Head of Business Engagement - Member of the Managing Board at World Economic Forum Geneva
**First published in weforum.org



.jpg)
 By: N. Peter Kramer
By: N. Peter Kramer